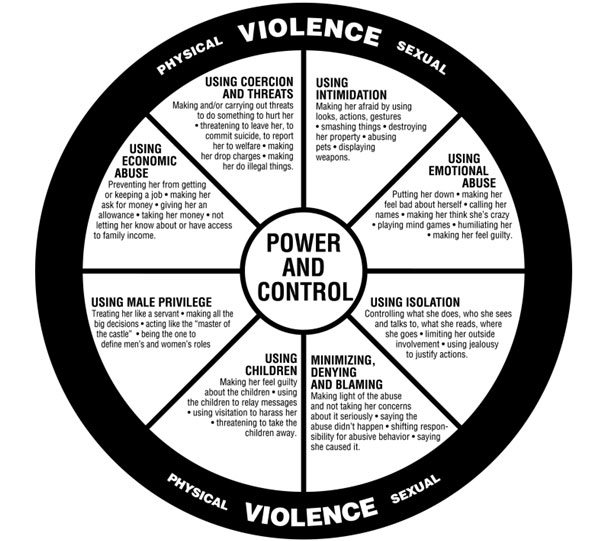
What is domestic violence? What “counts” as sexual assault? These are common questions we get regarding the work that we do and the people we serve. Before diving into each violence form specifically, it’s important to note the common theme: power and control.
In both domestic and sexual violence, it is power, control and domination that one partner in the relationship seeks over the other. The abuser can exercise dominance through multiple means: physically, psychologically, financially, relationally, sexually, spiritually, etc. The wheel below demonstrates how power and control can be achieved through different example tactics to ultimately achieve what we consider sexual and/or domestic violence. Other forms of power-based violence include dynamics where one person is able to gain and/or maintain power over the other, making the other vulnerable: